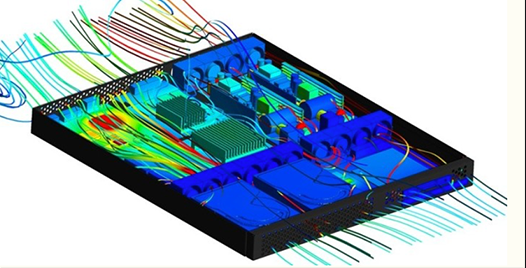
Forging heat sinks are a high-efficiency cooling device that uses advanced forging technology to increase the strength and stability of the heat sink and improve its cooling efficiency. Compared to traditional aluminum heat sinks, forging heat sinks can better adapt to the needs of high-power electronic devices and ensure that the devices remain cool under heavy loads.
The manufacturing process of forging heat sinks involves multiple steps, including mold design, forging, precision machining, and surface treatment. During the forging process, the surface of the heat sink fins can be compacted, improving the strength and stability of the heat sink. Additionally, forging heat sinks can utilize their unique internal structure to increase the surface area of the fins, thereby improving their cooling efficiency.
Another advantage of forging heat sinks is their lightweight design. Due to the use of forging technology, the heat sink structure is more compact and lightweight, making it better suited for portable electronic devices.
Forging heat sinks can also be made from different materials, such as copper, copper-nickel alloy, etc., to meet different environmental and performance requirements. These materials have better corrosion resistance and can extend the life of the heat sink.
In addition, forging heat sinks can be arranged in different ways, such as straight rows, horizontal rows, diamond arrangements, etc., to meet different cooling needs. These different arrangements can improve cooling efficiency and can be customized according to specific requirements.
Moreover, forging heat sinks can be combined with other cooling technologies, such as fans, liquid metal, heat pipes, etc., to further improve cooling efficiency and ensure stable operation of the device under heavy loads.
Overall, forging heat sinks are efficient, high-strength, stable, lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and customizable cooling solutions for high-power electronic devices. They are particularly suitable for industries such as computer hardware, telecommunications, aerospace, and automotive, where high-performance electronic systems require effective cooling solutions.